In the realm of industrial applications, selecting the appropriate wafer valve is crucial for ensuring efficient operations and maintaining system integrity. According to industry expert Dr. Michael Thompson, a renowned authority in fluid dynamics, "Choosing the right wafer valve is not just about compatibility; it's about enhancing the overall performance of the system." This statement underscores the importance of detailed consideration when making this vital choice, as wafer valves play a pivotal role in managing fluid flow, controlling pressure, and preventing leaks in various applications.
As industries continue to evolve, the demand for reliable and high-performing wafer valves has dramatically increased. With myriad options available, decision-makers must navigate through specifications such as material composition, size, pressure rating, and temperature tolerance to find the best fit for their specific needs. Understanding these parameters and their implications can make a significant difference in operational efficiency and long-term cost effectiveness. By leveraging insights from experts and staying informed about the latest advancements in wafer valve technology, businesses can make informed decisions that support their operational goals.

Wafer valves are essential components in various industrial applications, facilitating flow control in pipelines. These valves are characterized by their slim profile and lightweight design, allowing for easy installation between flanges without the need for additional support. Understanding the different types of wafer valves is crucial for selecting the right one for your specific needs. Common types include non-return valves, gate valves, and butterfly valves, each serving distinct purposes in managing fluid flow and preventing backflow.
The non-return valve, or check valve, automatically prevents backflow, ensuring that fluid flows in only one direction. It is particularly important in systems where reverse flow could cause damage or operational issues. Gate valves, on the other hand, are typically used for on-off control in larger pipelines. They provide minimal flow resistance when fully open and are best suited for applications requiring a straight-line flow. Butterfly valves are known for their ease of operation and are often used in situations where space is limited. Their design allows for quick throttling of flow, making them ideal for a variety of industries, including water treatment and chemical processing. Understanding these types of wafer valves will guide you in making informed decisions to optimize your industrial applications.
When selecting wafer valves for industrial applications, there are several key factors that must be taken into account. First and foremost is the valve’s compatibility with the media being handled. Different fluids, gases, and other materials can have unique properties that might affect the performance of the valve. It's essential to consider the chemical composition, temperature, and pressure conditions of the applications to ensure the selected wafer valve can withstand these factors without compromising functionality or safety.
Another crucial aspect to evaluate is the material construction of the valve itself. Wafer valves are fabricated from various materials, each with its own advantages and limitations. Evaluating the corrosion resistance, durability, and maintenance requirements of these materials will play a significant role in the valve's longevity and reliability in demanding environments. Additionally, understanding the operating mechanism of the valve is important; whether it’s a resilient seat, a blow-off valve, or a different design can influence how effectively it performs in your specific application. Ultimately, careful consideration of these factors will help ensure the right choice of wafer valve that aligns with operational needs and enhances overall system efficiency.
| Factor | Description | Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Material Compatibility | Ensure the valve material is compatible with the fluid being controlled. | Chemical resistance, temperature, and pressure ratings. |
| Size | Appropriate sizing for the specific flow requirements of the application. | Match with pipeline dimensions and flow rate. |
| Pressure Rating | Valves must be rated to withstand the maximum operating pressure. | Safety margins for pressure spikes. |
| Actuation Type | Decision between manual or automated actuators based on control needs. | Operator accessibility and automation requirements. |
| End Connection Type | Ensure proper connection style to match existing piping. | Flanged, threaded, or welded connections. |
| Flow Characteristics | Understand how the valve affects flow dynamics. | Check for pressure drop and flow control. |
| Maintenance and Serviceability | Consider ease of maintenance to ensure longevity. | Availability of replacement parts and service options. |
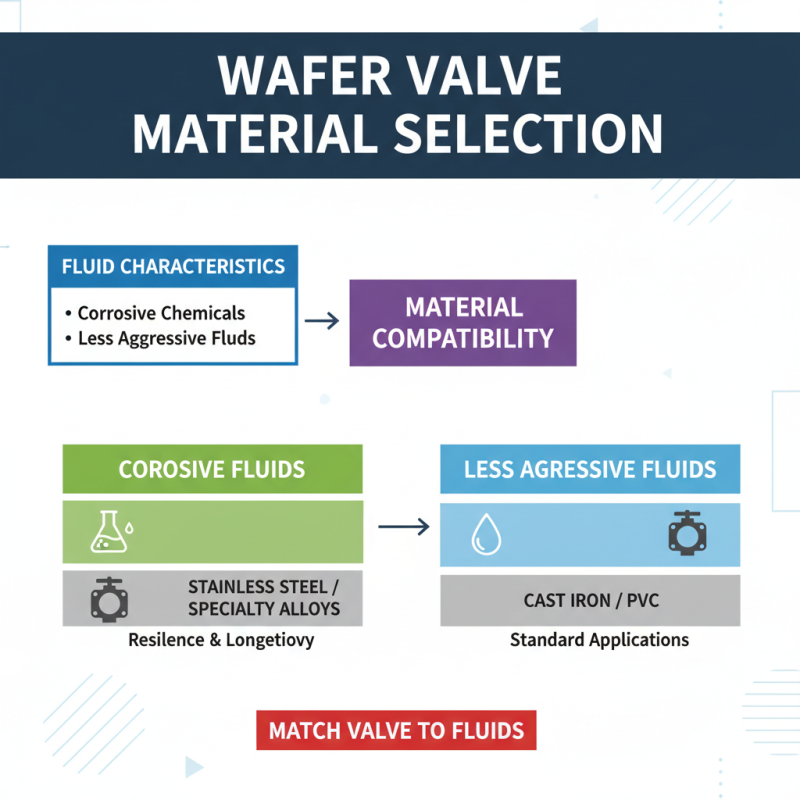
When selecting a wafer valve for industrial applications, material compatibility is a crucial consideration. The construction materials of the valve must align with the fluids it will encounter in the system. For instance, if the application involves corrosive chemicals, opting for stainless steel or specialized alloys can provide the resilience needed to prevent degradation and ensure longevity. For less aggressive environments, standard cast iron or PVC might suffice, but the key is to match the valve material with the specific characteristics of the fluids.
Tips: Always consult material data sheets to understand the chemical resistance of your chosen valve material. Conducting compatibility tests when uncertain can also help avert potential failures. Additionally, consider temperature and pressure ratings, as these factors, alongside fluid composition, determine the best material selection for optimal performance.
In some cases, factors like temperature fluctuations and pressure surges may impact the valve's performance over time. Choosing a valve with the right sealing materials, such as PTFE or EPDM, can enhance durability, particularly in extreme conditions. Careful evaluation of the operating environment will lead to more effective valve function and reduced maintenance costs, ultimately contributing to better system reliability.
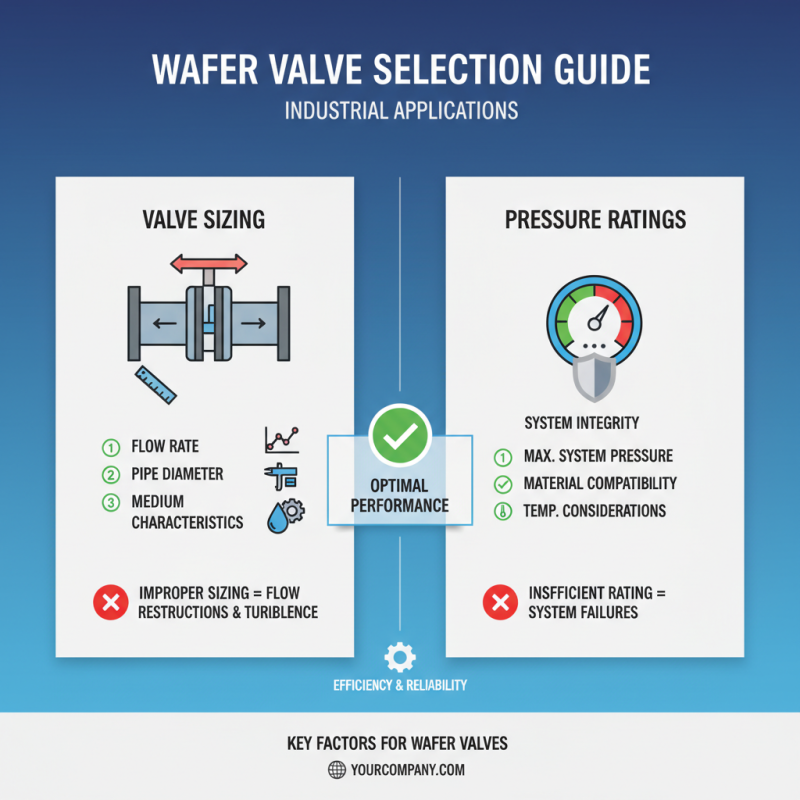
When selecting a wafer valve for industrial applications, understanding sizing and pressure ratings is essential for ensuring optimal performance. The size of the valve directly correlates with the flow rate and the system's overall efficiency. It is crucial to analyze the pipe diameter and the flow characteristics of the medium being transported. An improperly sized valve can lead to flow restrictions or excessive turbulence, resulting in increased operational costs and potential system failures.
Pressure ratings are another critical factor that must be considered in valve selection. Each valve is designed to operate within specific pressure limits, and exceeding these can compromise the valve’s integrity and cause hazardous leaks. Ensure that the selected wafer valve is compatible with the maximum expected operating pressure of your system. Consulting engineering guidelines can greatly aid in determining the appropriate pressure rating needed for safe and efficient operation.
**Tips:** Always refer to pressure-temperature ratings provided by valve manufacturers to ensure you’re choosing a valve that can withstand the specific conditions of your application. Additionally, consider the potential for pressure surges within your system, as these can affect performance and longevity. Regular maintenance checks and assessments can also help identify when a valve needs replacement or upgrading based on changing operational demands.
Wafer valves play a crucial role in various industrial applications, offering compact design and efficient flow control. These valves are widely used in sectors such as water treatment, food and beverage, chemical processing, and HVAC systems. The lightweight construction allows for easy installation in pipelines, where space may be limited. In water treatment facilities, wafer valves are employed to manage the flow of water efficiently, ensuring that the treatment processes run smoothly.
In the food and beverage industry, the sanitary design of wafer valves makes them ideal for handling liquids and gases without contamination. Their ability to maintain a tight seal is essential in preventing leaks and preserving product quality. Chemical processing industries benefit from wafer valves as they can withstand harsh chemicals and extreme temperatures, allowing for safe and reliable operations.
Tips: When selecting a wafer valve, consider the specific requirements of your application, including pressure, temperature, and the type of media being handled. It’s also important to assess the installation space and compatibility with existing piping systems to ensure optimal performance. Regular maintenance checks can help extend the lifespan of wafer valves, ensuring they function efficiently over time.






© Shipham Valves 2025. All Rights Reserved.
Website By PS Website Design Ltd
Request a Quote/Further Information
Download
We use cookies on this website, by continuing to browse the site you are agreeing to our use of cookies. Find out more.